Departments
Obstetrics and Gynaecology
Obstetrics and Gynaecology is the medical specialty that encompasses the two subspecialties of obstetrics (covering pregnancy, childbirth, and the postpartum period) and gynecology (covering the health of the female reproductive system – vagina, uterus, ovaries, and breasts).


Lorem Ipsum is simply dummy text of the printing and typesetting industry. Lorem Ipsum has been the industry’s standard dummy text ever since the 1500s, when an unknown printer took a galley of type and scrambled it to make a type specimen book. It has survived not only five centuries, but also the leap into electronic typesetting, remaining essentially unchanged. It was popularised in the 1960s with the release of Letraset sheets containing Lorem Ipsum passages, and more recently with desktop publishing software like Aldus PageMaker including versions of Lorem Ipsum.
Medical Centre
Medical centre is used for the purpose of providing professional health services (such as preventative care, diagnosis, medical or surgical treatment or counselling) to out-patients only, and includes health consulting rooms.


Lorem Ipsum is simply dummy text of the printing and typesetting industry. Lorem Ipsum has been the industry’s standard dummy text ever since the 1500s, when an unknown printer took a galley of type and scrambled it to make a type specimen book. It has survived not only five centuries, but also the leap into electronic typesetting, remaining essentially unchanged. It was popularised in the 1960s with the release of Letraset sheets containing Lorem Ipsum passages, and more recently with desktop publishing software like Aldus PageMaker including versions of Lorem Ipsum.
Surgery
Surgery is a medical specialty that uses operative manual and instrumental techniques on a person to investigate or treat a pathological condition such as a disease or injury, to help improve bodily function, appearance, or to repair unwanted ruptured areas.
The act of performing surgery may be called a surgical procedure, operation, or simply “surgery”. In this context, the verb “operate” means to perform surgery.
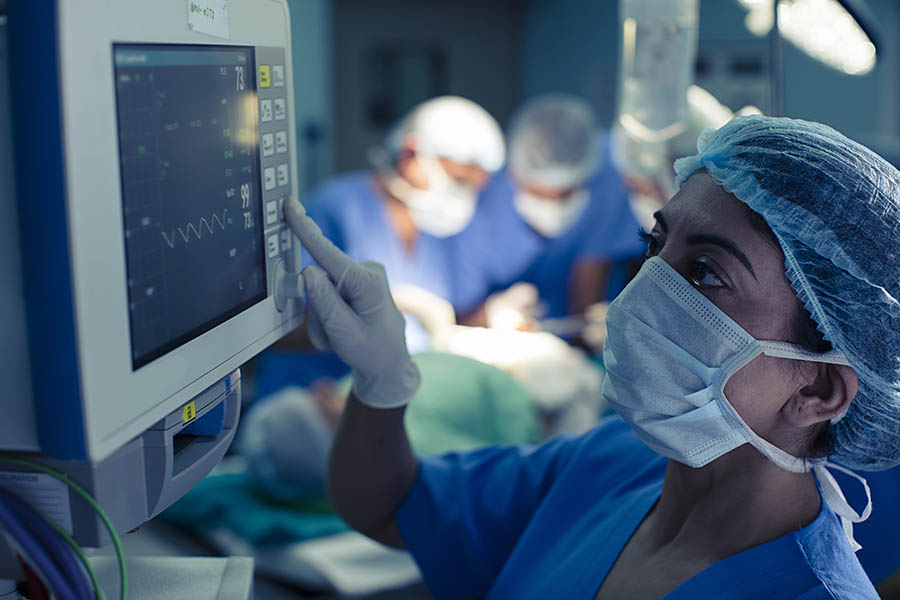

The person or subject on which the surgery is performed can be a person. A surgeon is a person who practices surgery and a surgeon’s assistant is a person who practices surgical assistance. A surgical team is made up of the surgeon, the surgeon’s assistant, an anaesthetist, a circulating nurse and a surgical technologist. Surgery usually spans from minutes to hours, but it is typically not an ongoing or periodic type of treatment.
ICU
The person or subject on which the surgery is performed can be a person. A surgeon is a person who practices surgery and a surgeon’s assistant is a person who practices surgical assistance. A surgical team is made up of the surgeon, the surgeon’s assistant, an anaesthetist, a circulating nurse and a surgical technologist. Surgery usually spans from minutes to hours, but it is typically not an ongoing or periodic type of treatment.

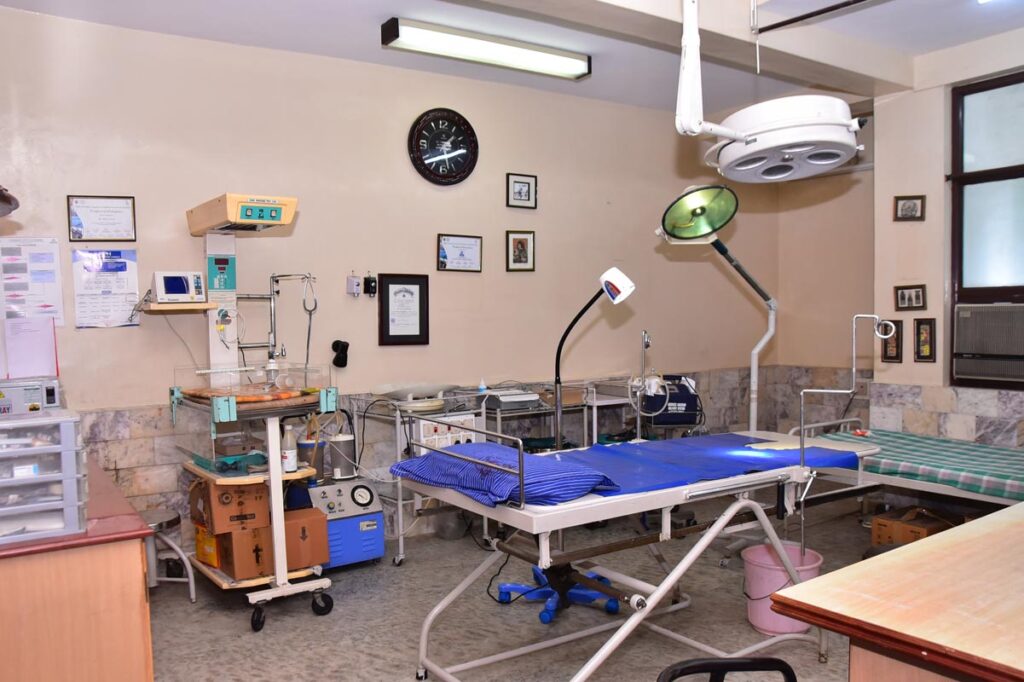
The person or subject on which the surgery is performed can be a person. A surgeon is a person who practices surgery and a surgeon’s assistant is a person who practices surgical assistance. A surgical team is made up of the surgeon, the surgeon’s assistant, an anaesthetist, a circulating nurse and a surgical technologist. Surgery usually spans from minutes to hours, but it is typically not an ongoing or periodic type of treatment.
Special Ward
A room in a hospital for the care of patients. types: ER, emergency room. a room in a hospital or clinic staffed and equipped to provide emergency care to persons requiring immediate medical treatment. OR, operating room, operating theater, operating theatre, surgery.

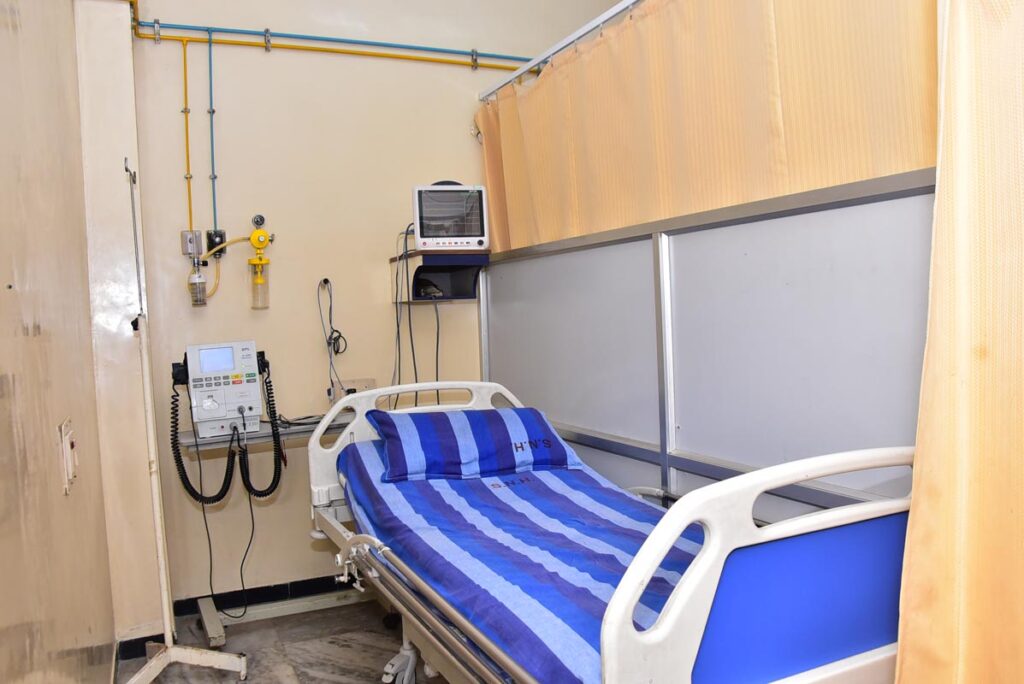
The person or subject on which the surgery is performed can be a person. A surgeon is a person who practices surgery and a surgeon’s assistant is a person who practices surgical assistance. A surgical team is made up of the surgeon, the surgeon’s assistant, an anaesthetist, a circulating nurse and a surgical technologist. Surgery usually spans from minutes to hours, but it is typically not an ongoing or periodic type of treatment.
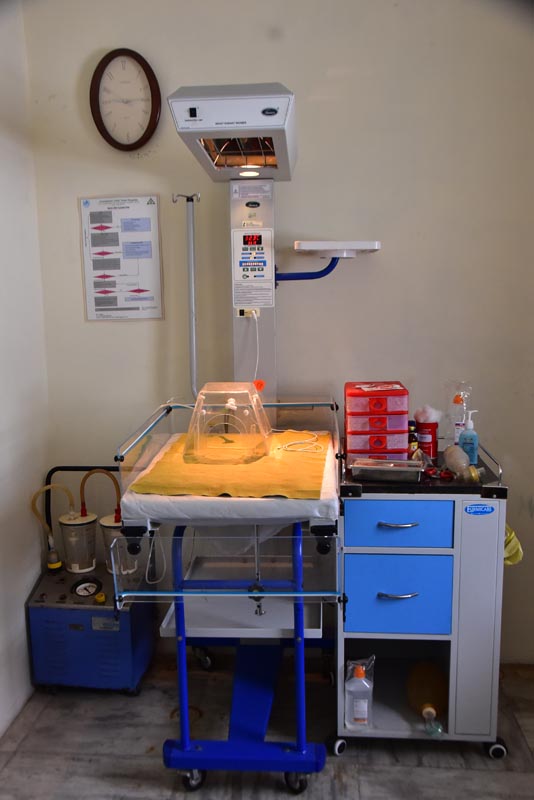
Birth Room
It is called a labor, delivery, and recovery room (LDR). This is the type of room that some hospitals and almost all birth centers use for their care. Once you are placed in a room, this is the room that you will use for your labor and birth, including the initial hours of recovery.
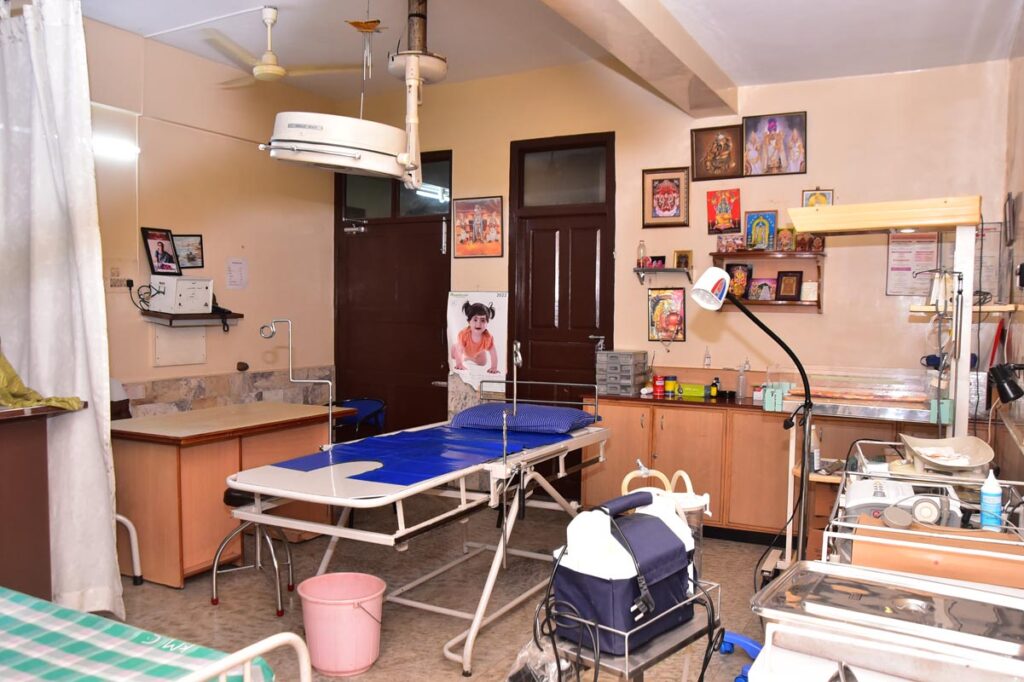

It is called a labor, delivery, and recovery room (LDR). This is the type of room that some hospitals and almost all birth centers use for their care. Once you are placed in a room, this is the room that you will use for your labor and birth, including the initial hours of recovery.
Dept. of O.G,
- Ultrasound and colonoscopy– can be done.
- Adolescent girls health
- Normal delivery-normal safe delivery with experienced staff and good level of care for the baby will be maintained
- Caesarean delivery-facilities for caesarean section is also available this can be planned or they can be done in case of failure of normal delivery maximum effort will be done to ensure normal delivery takes place
- Hysterectomy-Hysterectomy is the surgical removal of the uterus. It may also involve removal of the cervix, ovaries, Fallopian tubes, and other surrounding structures. Usually performed by a gynecologists’, a hysterectomy may be total or partial
- Infertility-What is infertility? In general, infertility is defined as not being able to get pregnant (conceive) after one year (or longer) of unprotected sex. Because fertility in women is known to decline steadily with age, some providers evaluate and treat women aged 35 years or older after 6 months of unprotected sex.
- Fibroids-Uterine fibroids are a common type of noncancerous tumour that can grow in and on your uterus. Not all fibroids cause symptoms, but when they do, symptoms can include heavy menstrual bleeding, back pain, frequent urination and pain during sex.
- Irregular periods-puberty –periods might be irregular for the first year or two. the start of the menopause (usually between the ages of 45 and 55)there is chance of irregular periods so a doctor’s visit may be necessary to evaluate all the possibilities
- Cervical insuffiency -An incompetent cervix, also called a cervical insufficiency, occurs when weak cervical tissue causes or contributes to premature birth or the loss of an otherwise healthy pregnancy. Before pregnancy, your cervix — the lower part of the uterus that opens to the vagina — is normally closed and firm
Dept. of General medicine
Fever
- A temporary increase in average body temperature of 98.6°F (37°C).
Echocardiogram
Hypertension
- A condition in which the force of the blood against the artery walls is too high.
- Usually hypertension is defined as blood pressure above 140/90, and is considered severe if the pressure is above 180/120.
- High blood pressure often has no symptoms. Over time, if untreated, it can cause health conditions, such as heart disease and stroke.
Diabetes mellitus
- Diabetes mellitus refers to a group of diseases that affect how the body uses blood sugar (glucose).
- Glucose is an important source of energy for the cells that make up the muscles and tissues.
- It’s also the brain’s main source of fuel.
Kidney problems
- You are at greater risk for kidney disease if you have diabetes or high blood pressure. If you experience kidney failure, treatments include kidney transplant or dialysis. Other kidney problems include acute kidney injury, kidney cysts, kidney stones, and kidney infections.
- Jaundice Yellow skin caused by the build-up of bilirubin in the blood.
- Jaundice may occur if the liver can’t efficiently process red blood cells as they break down. It’s normal in healthy newborns and usually clears on its own. At other ages, it may signal infection or liver disease.
- Symptoms include yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes.
- Some newborns may require light therapy for a day or so. In other cases, treatment involves addressing the underlying cause
Anemia
- A condition in which the blood doesn’t have enough healthy red blood cells.
- Anemia results from a lack of red blood cells or dysfunctional red blood cells in the body. This leads to reduced oxygen flow to the body’s organs
- Symptoms may include fatigue, skin pallor, shortness of breath, light-headedness, dizziness or a fast heartbeat.
- Treatment depends on the underlying diagnosis. Iron supplements can be used for iron deficiency. Vitamin B supplements may be used for low vitamin levels. Blood transfusions can be used for blood loss. Medication to induce blood formation may be used if the body’s blood production is reduced
High cholesterol
- High amounts of cholesterol in the blood.
- High cholesterol can limit blood flow, increasing the risk of a heart attack or stroke. It’s detected by a blood test.
- High cholesterol has no symptoms.
- Treatments include medication, a healthy diet and exercise.
Heart attack
- A blockage of blood flow to the heart muscle.
- A heart attack is a medical emergency. A heart attack usually occurs when a blood clot blocks blood flow to the heart. Without blood, tissue loses oxygen and dies.
- Symptoms include tightness or pain in the chest, neck, back or arms, as well as fatigue, light-headedness, abnormal heartbeat and anxiety. Women are more likely to have atypical symptoms than men.
- Treatment ranges from lifestyle changes and cardiac rehabilitation to medication, stents and bypass surgery
Tuberculosis
- A potentially serious infectious bacterial disease that mainly affects the lungs.
- The bacteria that cause TB are spread when an infected person coughs or sneezes.
- Most people infected with the bacteria that cause tuberculosis don’t have symptoms. When symptoms do occur, they usually include a cough (sometimes blood-tinged), weight loss, night sweats and fever.
- Treatment isn’t always required for those without symptoms. Patients with active symptoms will require a long course of treatment involving multiple antibiotics.
COPD
- A group of lung diseases that block airflow and make it difficult to breathe.
- Emphysema and chronic bronchitis are the most common conditions that make up COPD. Damage to the lungs from COPD can’t be reversed.
- Symptoms include shortness of breath, wheezing or a chronic cough.
- Rescue inhalers and inhaled or oral steroids can help control symptoms and minimize further damage
Dept. of Gen Surgery,
- Diabetic foot management diabetic foot requires extensive foot care with our excellent nursing care and post op follow up this is made much easier
- Cancer surgery-surgery for various cancers are done here
- Laparoscopic surgery Laparoscopy is a type of surgical procedure that allows a surgeon to access the inside of the abdomen (tummy) and pelvis without having to make large incisions in the skin. This procedure is also known as keyhole surgery or minimally invasive surgery.
- This allows for minimal scar tissue and cosmetically better appearance
- Varicose veins surgery varicose veins are twisted enlarged veins, Any vein that is close to the skin’s surface (superficial) can become varicose. Varicose veins most commonly affect the veins in the legs. That’s because standing and walking increases the pressure in the veins of the lower body.
Labour Room
Once the baby is born, there is equipment in the room to handle newborn care as well. While the immediate care of the newborn is best handled via skin to skin with the mother, if there were an emergency or the need for specialized equipment, the average LDR room is prepared with a warmer for the baby and life-saving resuscitation equipment. You stay in this room for the first hour or two after you give birth, then transferred to a postpartum room.
LDRP Rooms
Some facilities also offer what is called a Labor, Delivery, Recovery, and Postpartum (LDRP) room. In the LDRP, you will give birth here and your baby will stay with you until you are ready to go home. Many of these facilities use the nursery only for babies who are ill, rather than for well newborn care.
As with the LDR, the LDRP is equipped to handle only vaginal births. You can have an epidural or other pain medication in this room if they are available at your place of birth. And, if you are in a hospital and require it, you may also have a forceps or vacuum delivery in the vast majority of LDRP rooms. If you require a c-section at the hospital, you will generally not recover in the LDR or the LDRP, even if you labored in one. This may depend on space and the number of people on shift.

It is called a labor, delivery, and recovery room (LDR). This is the type of room that some hospitals and almost all birth centers use for their care. Once you are placed in a room, this is the room that you will use for your labor and birth, including the initial hours of recovery.
Dept of physcaitry
- Schizophrenia spectrum and other psychotic disorders.-Schizophrenia is a serious mental disorder in which people interpret reality abnormally. Schizophrenia may result in some combination of hallucinations, delusions, and extremely disordered thinking and behavior that impairs daily functioning, and can be disabling. People with schizophrenia require lifelong treatment.
- Bipolar and related disorders-A disorder associated with episodes of mood swings ranging from depressive lows to manic highs.
- The exact cause of bipolar disorder isn’t known, but a combination of genetics, environment and altered brain structure and chemistry may play a role.
- Manic episodes may include symptoms such as high energy, reduced need for sleep and loss of touch with reality. Depressive episodes may include symptoms such as low energy, low motivation and loss of interest in daily activities. Mood episodes last days to months at a time and may also be associated with suicidal thoughts.
- Treatment is usually lifelong and often involves a combination of medications and psychotherapy
Trauma- and stressor–related disorders
- A disorder characterized by failure to recover after experiencing or witnessing a terrifying event.
- The condition may last months or years, with triggers that can bring back memories of the trauma accompanied by intense emotional and physical reactions.
- Symptoms may include nightmares or flashbacks, avoidance of situations that bring back the trauma, heightened reactivity to stimuli, anxiety or depressed mood.
- Treatment includes different types of psychotherapy as well as medications to manage symptoms.
Obsessive-compulsive and related disorders
- Excessive thoughts (obsessions) that lead to repetitive behaviors (compulsions).
- Obsessive-compulsive disorder is characterized by unreasonable thoughts and fears (obsessions) that lead to compulsive behaviors.
- OCD often centers on themes such as a fear of germs or the need to arrange objects in a specific manner. Symptoms usually begin gradually and vary throughout life.
- Treatment includes talk therapy, medication or both.
Depressive disorders
- A mental health disorder characterized by persistently depressed mood or loss of interest in activities, causing significant impairment in daily life.
- Possible causes include a combination of biological, psychological and social sources of distress. Increasingly, research suggests that these factors may cause changes in brain function, including altered activity of certain neural circuits in the brain.
- The persistent feeling of sadness or loss of interest that characterizes major depression can lead to a range of behavioral and physical symptoms. These may include changes in sleep, appetite, energy level, concentration, daily behaviour or self-esteem. Depression can also be associated with thoughts of suicide.
- The mainstay of treatment is usually medication, talk therapy or a combination of the two. Increasingly, research suggests that these treatments may normalize brain changes associated with depression.
Anxiety disorders
- Anxiety disorder due to a medical condition includes symptoms of intense anxiety or panic that are directly caused by a physical health problem. Generalized anxiety disorder includes persistent and excessive anxiety and worry about activities or events — even ordinary, routine issues.
Feeding and eating disorders problems with sucking, eating from a spoon, chewing, or drinking from a cup. Swallowing disorders, also called dysphagia (dis-FAY-juh) are difficulties with moving food or liquid from the mouth, throat, or esophagus to the stomach.
Deaddiction from smoking and alcohol
- Excessive use of psychoactive drugs, such as alcohol, pain medications or illegal drugs. It can lead to physical, social or emotional harm.
Operation Theatre
An operating theater (also known as an operating room (OR), operating suite, or operation suite) is a facility within a hospital where surgical operations are carried out in an aseptic environment.
Historically, the term “operating theater” referred to a non-sterile, tiered theater or amphitheater in which students and other spectators could watch surgeons perform surgery. Contemporary operating rooms are usually devoid of a theater setting, making the term “operating theater” a misnomer in those cases.


Operating rooms are spacious, in a cleanroom, and well-lit, typically with overhead surgical lights, and may have viewing screens and monitors. Operating rooms are generally windowless, though windows are becoming more prevalent in newly built theaters to provide clinical teams with natural light, and feature controlled temperature and humidity. Special air handlers filter the air and maintain a slightly elevated pressure. Electricity support has backup systems in case of a black-out. Rooms are supplied with wall suction, oxygen, and possibly other anesthetic gases.
Key equipment consists of the operating table and the anesthesia cart. In addition, there are tables to set up instruments. There is storage space for common surgical supplies. There are containers for disposables. Outside the operating room, or sometimes integrated within, is a dedicated scrubbing area that is used by surgeons, anesthetists, ODPs (operating department practitioners), and nurses prior to surgery. An operating room will have a map to enable the terminal cleaner to realign the operating table and equipment to the desired layout during cleaning. Operating rooms are typically supported by an anaesthetic room, prep room, scrub and a dirty utility room.
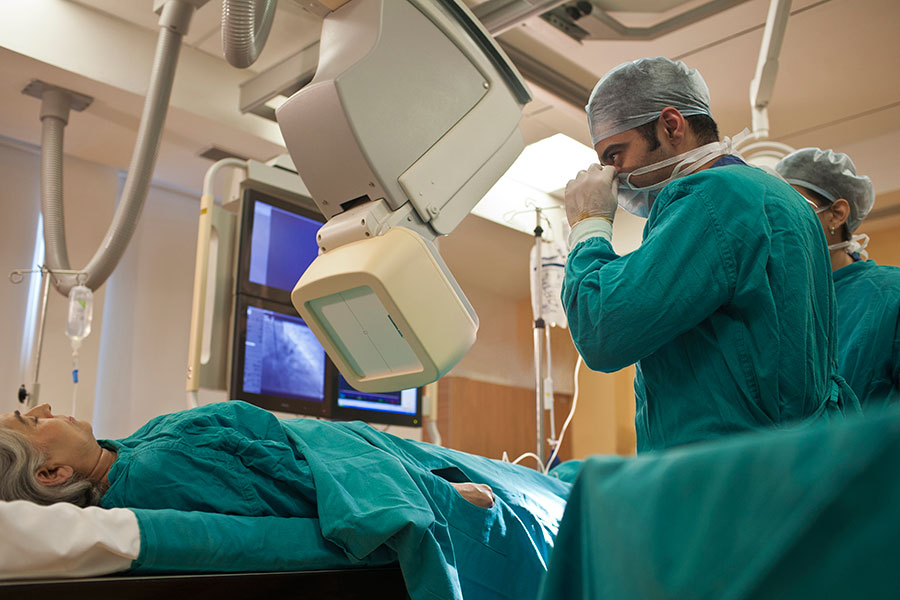

Several operating rooms are part of the operating suite that forms a distinct section within a health-care facility. Besides the operating rooms and their wash rooms, it contains rooms for personnel to change, wash, and rest, preparation and recovery rooms(s), storage and cleaning facilities, offices, dedicated corridors, and possibly other supportive units. In larger facilities, the operating suite is climate- and air-controlled, and separated from other departments so that only authorized personnel have access.
Ent
Otorhinolaryngology is a surgical subspecialty within medicine that deals with the surgical and medical management of conditions of the head and neck. Doctors who specialize in this area are called otorhinolaryngologists, otolaryngologists, head and neck surgeons, or ENT surgeons or physicians.
